TEST: Intel Solidigm P44 Pro 1TB M.2 SSD
Here you can find a detailed performance and benchmark test of the M.2 NVMe SSD Solidigm P44 Pro with 1TB (SSDPFKKW010X7X1) from Intel.9191
0,22 $
| Technical data | |
| Image | 
|
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Model number | SSDPFKKW010X7X1 |
| Storage capacity | 1024 GB (954 GiB) |
| pSLC-Cache | 184 GB approx. |
| Read speed | 7000 MB/s |
| Write speed | 6500 MB/s |
| Interface | PCIe 4.0 x4 |
| Connection | M.2 2280 |
| Memory module (NAND) | TLC |
| DRAM Cache | ✓ yes |
| TBW (Total Bytes Written) | 750 Terabyte |
| Controller | SK Hynix Aries |
| Price | ca. 224 USD (= 0,22 $ / GB) |
| Paid link | Buy on Amazon |
Compared to the top performer*
*) Test result evaluated according to AS SSD Score within the same size.
AS SSD Benchmark
Standard performance test
The standard test was performed using a 5 GB file. A total score of 9191 points was achieved.

| AS SSD | Read: | Write: |
|---|---|---|
| Seq in megabytes per second |
6103,57 MB/s |
5677,15 MB/s |
| 4K in megabytes per second |
74,54 MB/s |
205,38 MB/s |
| 4K-64Thrd in megabytes per second |
2837,22 MB/s |
3119,23 MB/s |
| Access time in milliseconds |
0,018 ms |
0,092 ms |
| Score | 3522 |
3892 |
| Total score | 9191 |
|
Copy Performance Test
A common everyday situation is simulated here. Three test folders are created:
- ISO (folder with two large files)
- Program (folder with many small files)
- Game (folder with small and large files)
The three folders are copied using the Windows Copy command (the cache remains enabled). The practical test of May 10, 2023 shows the performance for simultaneous write and read operations. The lower the duration, the better the performance.
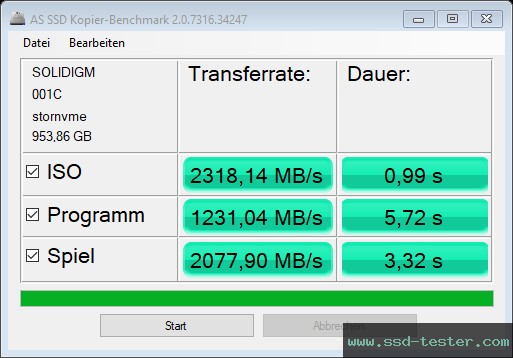
| AS SSD Copy-Benchmark | Transfer rate: | Duration: |
|---|---|---|
| ISO two large files |
2318,14 MB/s |
0,99 s |
| Program many small files |
1231,04 MB/s |
5,72 s |
| Game small and large files |
2077,90 MB/s |
3,32 s |
Compression Performance Test
This measures the write and read speed of the Intel SSD, depending on the compressibility of the data (according to the manufacturer, these should be 7000 MB/s and 6500 MB/s respectively ).

CrystalDiskMark Benchmark
Here, two sequential and two random performance tests are performed, similar to the ones performed on the AS SSD.

| CDM | Read [MB/s] | Write [MB/s] |
|---|---|---|
| SEQ1M Q8T1 |
7350,33 |
6660,81 |
| SEQ1M Q1T1 |
5705,01 |
5151,45 |
| RND4K Q32T16 |
3683,72 |
3021,78 |
| RND4K Q1T1 |
73,38 |
227,70 |
Input/Output operations per second
| CDM | Read [IOPS] | Write [IOPS] |
|---|---|---|
| SEQ1M Q8T1 |
7.009,80 |
6.352,20 |
| SEQ1M Q1T1 |
5.440,70 |
4.912,80 |
| RND4K Q32T16 |
899.346,00 |
737.738,00 |
| RND4K Q1T1 |
17.916,00 |
55.591,80 |
Average latency
| CDM | Read [µs] | Write [µs] |
|---|---|---|
| SEQ1M Q8T1 |
1.140,14 |
1.256,66 |
| SEQ1M Q1T1 |
183,60 |
203,34 |
| RND4K Q32T16 |
551,03 |
685,46 |
| RND4K Q1T1 |
55,71 |
17,87 |
HD Tune Pro Endurance test
This is a long term test to make full use of the memory capacity. You can see when a cache is full and the writing performance decreases.
A test file of 200 GB was written to the medium.
After approx. 184 GB, the pSLC-Cache was full and the performance was throttled.
The average read speed was 6217 MB/s and the average write speed was 4652 MB/s.
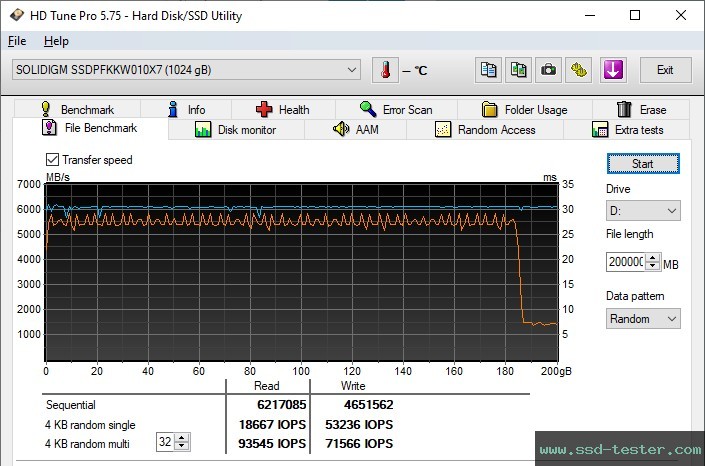
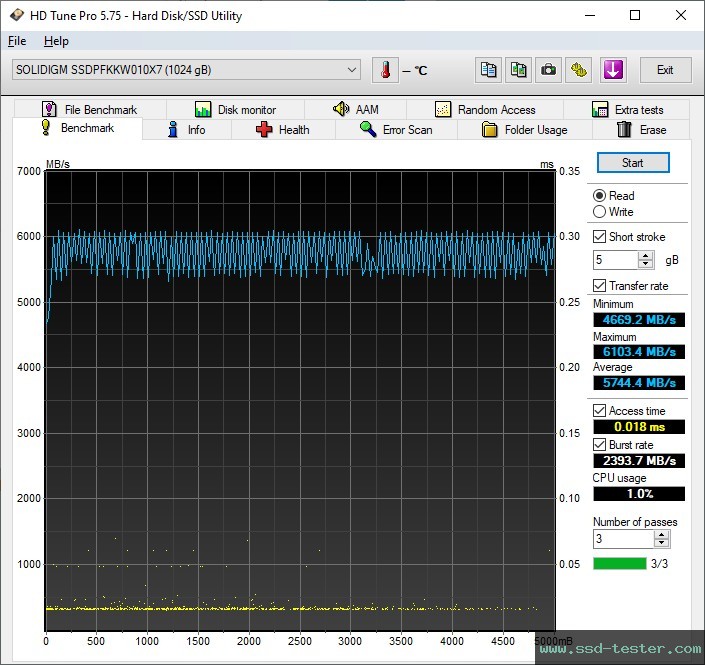
HD Tune Pro Benchmark
HD Tune writes a 5 GB file to the Intel M.2 SSD. The transfer data of the read speed is displayed graphically. The minimum, maximum and average values are also determined. The determined access time and burst rate are also displayed.
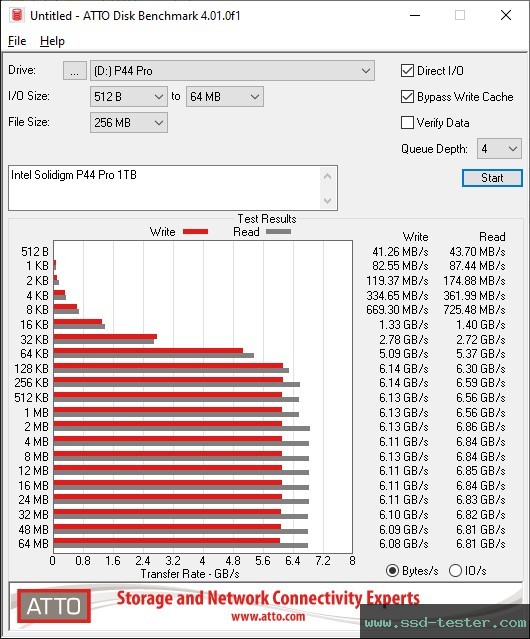
ATTO Disk Benchmark
Here, a 256 MB file is written several times to the Intel M.2 SSD. The I/O block size varies (from 512 bytes to 64 megabytes). The larger the blocks, the faster they were written and read.
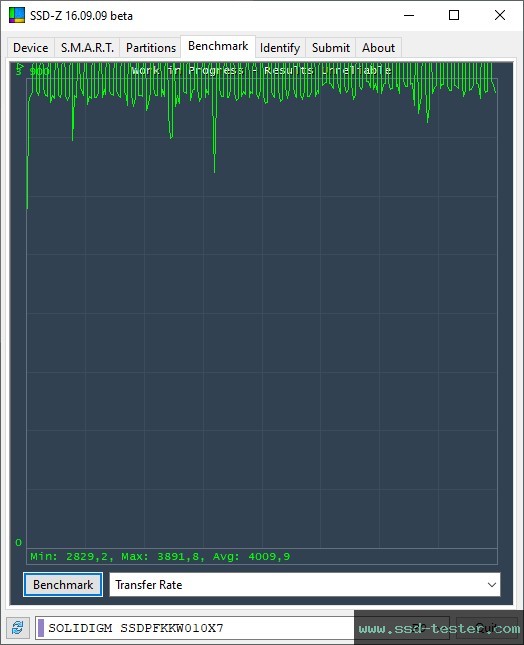
SSD-Z Benchmark
Similar to HD Tune, a 500 MB file is written to the Intel M.2 SSD here. The transfer data is displayed. The more constant the line, the better. Unfortunately, the tool does not work correctly above about 5,000 MB/s and no line (and sometimes wrong min and max data) is displayed.
Information about the test system can be found at the bottom of the home page.
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.